What is dual stream technology?
In networked video surveillance, after the analog audio and video signals are imaged, collected, and coded, the digital audio and video streams transmitted over the network are commonly referred to as "streams." The two most important indicators that affect the quality of video streaming are "video resolution" and "video bit rate."
Video resolution refers to the amount of information stored in each frame of an image, measured in pixels per inch (PPI). Currently, the mainstream resolutions in the surveillance area are 1080p (1920×1080), 720p (1280×720), and D1 (704*576), and 5 million, 8 million, and 4K are gradually entering the eyes of people.
Corresponding to the video resolution, the video bit rate refers to the rate at which the video stream transmits data in the channel, in units of bits per second (bits per second), which indicates the bandwidth occupied by the video stream in the network transmission.
Under normal circumstances, the greater the video resolution, the larger the video bit rate and the clearer the picture, but in proportion to this, the bandwidth that the video bitstream occupies in the network transmission is also greater, and the video decoding display is occupied. The more system resources are. Therefore, when the video resolution used by the video surveillance is getting higher and higher, the existing internetwork can hardly bear the video stream with too large bitrate, and the existing computer also has performance when multi-channel decoding is performed on high-resolution video. The bottleneck. In order to solve this problem, the concept of "dual stream" came into being. Dual stream, as the name implies, encodes the same video source into two streams. The two streams can be of the same resolution or different resolutions.
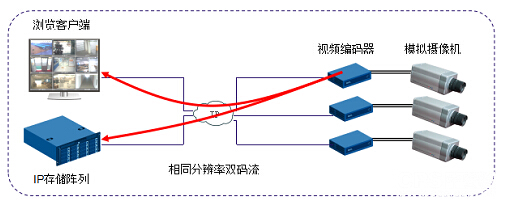
Some manufacturers of network video front-end can be programmed with the same resolution of the two streams, respectively, to the browser client and storage server. This encoding and transmission method can fully reduce the pressure of the monitoring host's code stream forwarding, but it is very easy to cause network congestion and can only be used in occasions where the network bandwidth is very abundant. As shown below:
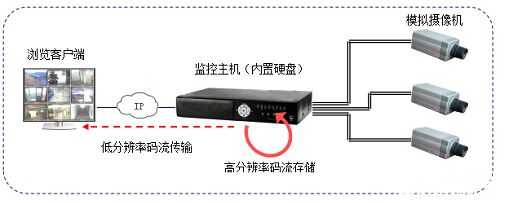
Some manufacturers' network video front-ends can encode two streams with different resolutions. The larger-resolution stream is used for video storage, and the lower-resolution stream is used for real-time browsing. This can fully reduce the pressure of network bandwidth occupied by remote browsing, but the usage is not flexible enough. Users can only browse low-resolution images when the bandwidth is sufficient. As shown below:
Based on the advantages and disadvantages of the above two methods, many manufacturers set the NVR dual stream to be more flexible. The NVR cooperates with the network front end and can compile two streams with different resolutions. The high resolution stream is used as the NVR local storage. In real-time browsing, it can be automatically adjusted according to the size of the user's browsing screen and the network bandwidth of the user. . For example: Set the high-resolution stream to 720P, then the real-time browsing stream can be automatically adjusted in 720P, D1 and smaller resolution. This dual stream setup has two advantages:
1. In the case of the same video resolution, the resolution can be automatically adjusted according to the user's actual bandwidth, so that narrow-band users can use low-resolution video browsing, while users with more bandwidth have higher resolution. For video browsing.
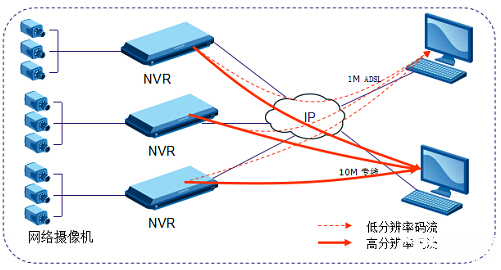
2. In the case of the same video resolution, the resolution can be automatically adjusted according to the way the user uses the screen segmentation of the client. When the user browses the large screen, the high-resolution stream is transmitted, and the user is performing a small screen. While browsing, the low resolution stream is transmitted. This can fully improve the decoding efficiency of the computer used by the user.

Utilizing the dual-stream feature of the NVR, flexible settings can be made according to different situations, more in line with the requirements of networked video transmission, and it is also possible to achieve more simultaneous video browsing without increasing the performance of the computer. Will affect the quality of video recordings.
Video resolution refers to the amount of information stored in each frame of an image, measured in pixels per inch (PPI). Currently, the mainstream resolutions in the surveillance area are 1080p (1920×1080), 720p (1280×720), and D1 (704*576), and 5 million, 8 million, and 4K are gradually entering the eyes of people.
Corresponding to the video resolution, the video bit rate refers to the rate at which the video stream transmits data in the channel, in units of bits per second (bits per second), which indicates the bandwidth occupied by the video stream in the network transmission.
Under normal circumstances, the greater the video resolution, the larger the video bit rate and the clearer the picture, but in proportion to this, the bandwidth that the video bitstream occupies in the network transmission is also greater, and the video decoding display is occupied. The more system resources are. Therefore, when the video resolution used by the video surveillance is getting higher and higher, the existing internetwork can hardly bear the video stream with too large bitrate, and the existing computer also has performance when multi-channel decoding is performed on high-resolution video. The bottleneck. In order to solve this problem, the concept of "dual stream" came into being. Dual stream, as the name implies, encodes the same video source into two streams. The two streams can be of the same resolution or different resolutions.
Some manufacturers of network video front-end can be programmed with the same resolution of the two streams, respectively, to the browser client and storage server. This encoding and transmission method can fully reduce the pressure of the monitoring host's code stream forwarding, but it is very easy to cause network congestion and can only be used in occasions where the network bandwidth is very abundant. As shown below:

Some manufacturers' network video front-ends can encode two streams with different resolutions. The larger-resolution stream is used for video storage, and the lower-resolution stream is used for real-time browsing. This can fully reduce the pressure of network bandwidth occupied by remote browsing, but the usage is not flexible enough. Users can only browse low-resolution images when the bandwidth is sufficient. As shown below:

Based on the advantages and disadvantages of the above two methods, many manufacturers set the NVR dual stream to be more flexible. The NVR cooperates with the network front end and can compile two streams with different resolutions. The high resolution stream is used as the NVR local storage. In real-time browsing, it can be automatically adjusted according to the size of the user's browsing screen and the network bandwidth of the user. . For example: Set the high-resolution stream to 720P, then the real-time browsing stream can be automatically adjusted in 720P, D1 and smaller resolution. This dual stream setup has two advantages:
1. In the case of the same video resolution, the resolution can be automatically adjusted according to the user's actual bandwidth, so that narrow-band users can use low-resolution video browsing, while users with more bandwidth have higher resolution. For video browsing.

2. In the case of the same video resolution, the resolution can be automatically adjusted according to the way the user uses the screen segmentation of the client. When the user browses the large screen, the high-resolution stream is transmitted, and the user is performing a small screen. While browsing, the low resolution stream is transmitted. This can fully improve the decoding efficiency of the computer used by the user.

Utilizing the dual-stream feature of the NVR, flexible settings can be made according to different situations, more in line with the requirements of networked video transmission, and it is also possible to achieve more simultaneous video browsing without increasing the performance of the computer. Will affect the quality of video recordings.
The screen printing squeegee is an essential tool in the field of screen printing. They are used to push ink evenly through the mesh screen and onto the printing surface, ensuring high quality and consistent printing. There are many types of screen printing squeegees, including wooden squeegees, manual squeegees, rubber squeegees, and aluminum squeegees, and each squeegee has a specific purpose in the screen printing process.
Wood screen printing squeegee are a popular choice among screen printers due to their durability and flexibility. The wooden handle provides a comfortable grip for precise control during the printing process. The flexibility of the wood allows for smooth, even application of pressure, resulting in an even print.
Manual Wood Screen Printing Hand Squeegee are another variation of wooden squeegees designed to be handheld for more complex and detailed printing. These squeegees are ideal for smaller print runs and designs that require precision and attention to detail.
Wood Screen Printing Squeegee,Manual Wood Screen Printing Hand Squeegee,Aluminum Screen Printing Squeegee,Squeegee Rubber
Lauer Water-Based New Material(Foshan)Co.,Ltd. , https://www.lauerink.com